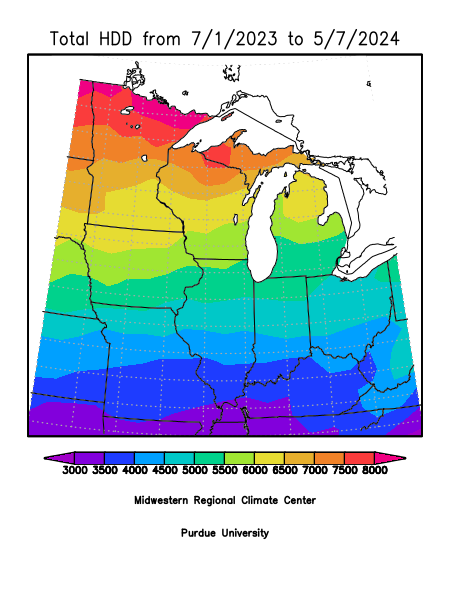
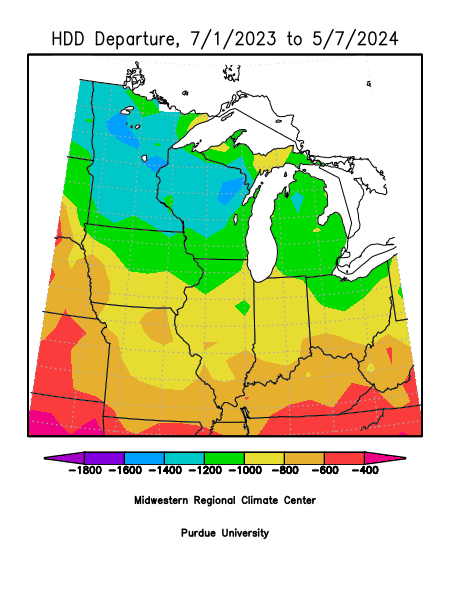
Heating Degree Days
Heating Degree Days (HDD) are a measure used to estimate the energy needed to heat buildings. HDDs are calculated by determining how many degrees the average daily temperature falls below a baseline temperature, typically 65°F in the U.S.
For example, if the average temperature for a day is 55°F, there would be 10 heating degree days (65 - 55 = 10). The more HDDs accumulated over a period, the more heating is required to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. HDDs are used by utility companies, HVAC professionals, and building managers to predict energy consumption, plan for heating needs, and analyze weather impacts on energy use.
Click maps for full image.